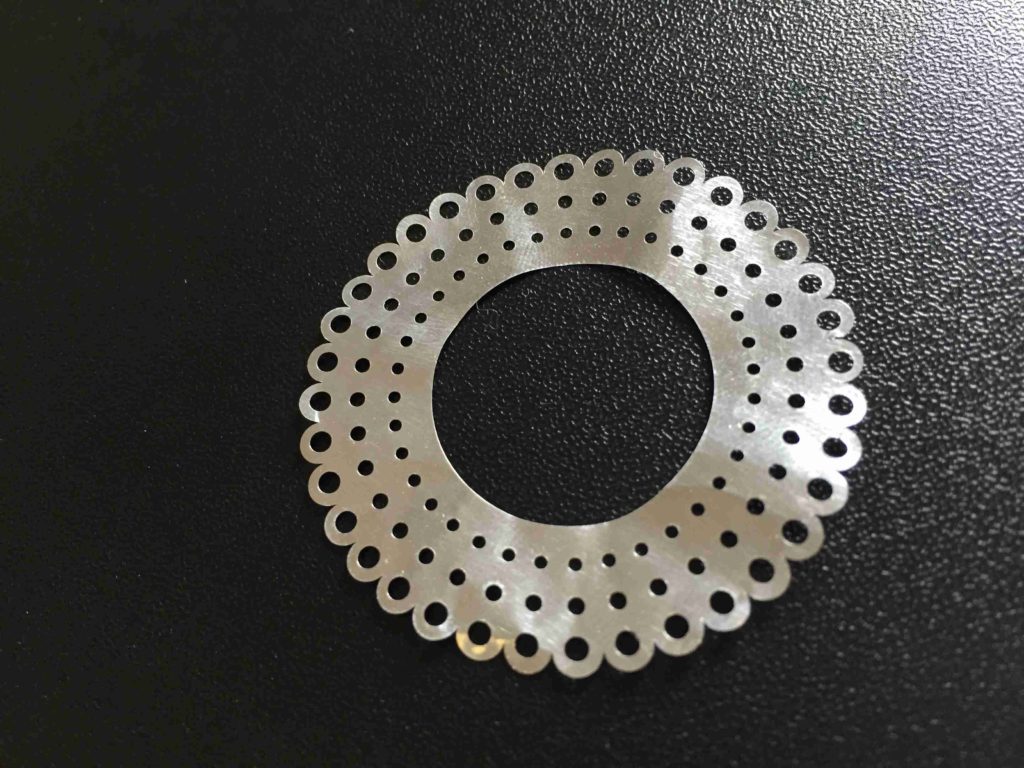
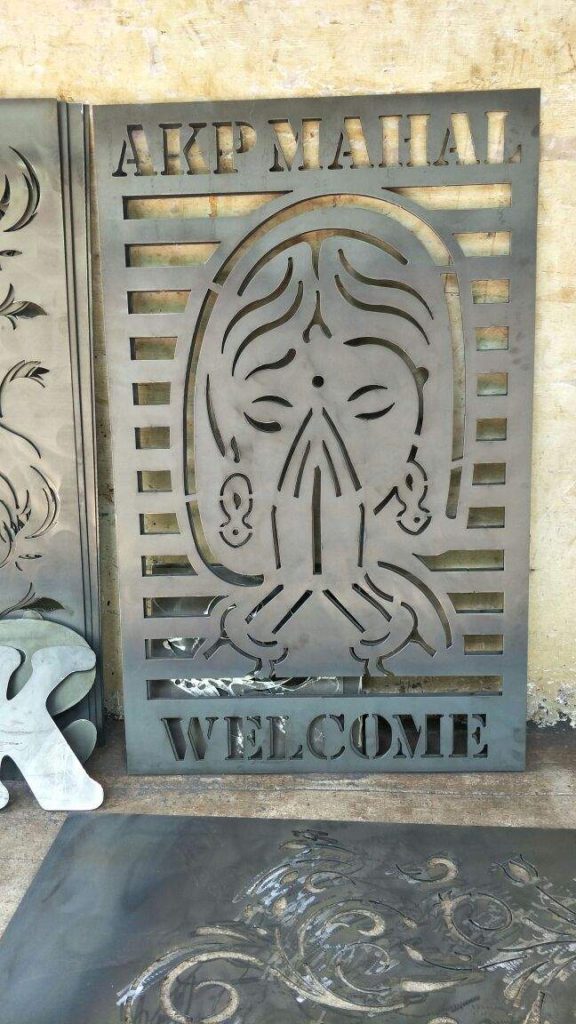
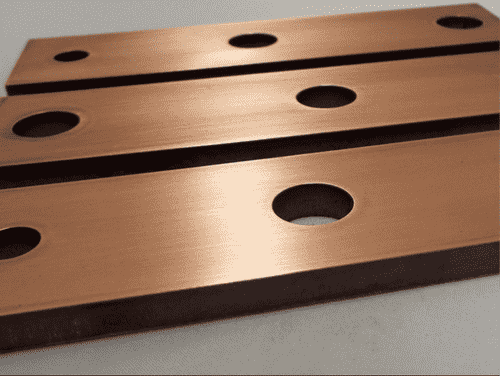
Hindcam offers Laser Cutting Job Work over metallic surfaces with higher-quality and high-precision work. It includes steel, Mild Steel, Stainless Steel, Aluminum, Copper, Brass, and so on. Also, you will see quality work in highly reflective materials without any deformity and with precision of work. So, here we will see how it works and its refined samples which we have taken during the operations.
Machine’s Info

- Cutting Capacity
- MS: 12 mm
SS: 6 mm
Aluminum: 4mm
Copper: 3mm
Brass: 3mm
Call/ WhatsApp: 9804-716-716
Characteristics of laser metal cutting works capabilities
- Copper laser cutting: We can cut upto 2 mm copper sheet. Maximum sheet size supported is 1500 x 2500 mm. Copper laser cutting is done using high pressure dry Air. The cutting capacity is lower in copper because it is highly reflective metal. To know more read here: Copper laser cutting
- Brass Laser cutting: Brass behaves just like copper under laser cutting machines. Max cutting thickness is 2 mm or less. Like copper brass is also cut using high pressure air (or optionally Nitrogen).
- MS laser cutting: We can cut mild steel upto 12 mm. upto 2 mm MS is cut using High pressure dry air. 3 mm can be cut using both Air and oxygen. 4 mm to 12 mm is cut using low pressure oxygen.
- Stainless steel laser cutting: Stainless steel is cut using compressed dry Air. Optionally it can also be cut using Nitrogen. However cutting with nitrogen would increase cost of cutting. We can cut up-to 6 mm Stainless Steel. You can get more idea here: Stainless Steel (SS) Laser Cutting
The high-precision laser metal cutting accuracy is up to 0.01. Here is the cutting accuracy and material thickness level, which you can expect from a laser cutting machine.
| Material | Material thickness (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 3.5 | 6 | |
| Stainless steel | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 500 | 250 |
| Aluminum | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 3800 | 10000 |
| Mild steel | – | 400 | – | 500 | – |
| Titanium | 250 | 210 | 210 | – | – |
Application of laser cutting
Laser cutting of metal is widely used in Fabrication, Gate and Grill design, Sheet metal covering, sheet metal components, and Custom metal stencils. However, for better application assistance services and usability preferences, you can go with further below points:
- Mold and tooling industry: Lasers are used in molds for duplicate parts. In addition, it is widely used in automobile and manufacturing industries, where tools and accessories need to get cut. Here, very precise cutting over the SS sheet, aluminum, and brass, tools are cut for multi-applications.
- Jewelry designing: In jewelry industries, designing, cutting, and modifications of the gold, silver, and platinum materials are done. It includes designing, and cutting for rings, bracelets, necklace designing, and complex cuttings and the list continues.
- Ceramics making industries: To get high-quality and finished edges quality and specified cutting area. You can easily see its work-precision in Aircraft products, dual-speakers, headphones, power plant generators, etc.
- Medical products manufacturing: It includes many high-end medical parts like valve frames, vascular clips, etc.
- Outdoor and indoors units: It includes kitchen cabinets, doors, hinges, windows, almirah, boundaries , railings etc.
Laser Cutting Theory and Working Principle
Laser metal cutting is a highly precise and efficient technique used to cut metal sheets and other metal materials. It utilizes the energy of a laser beam to melt, burn, or vaporize the metal, resulting in a clean and accurate cut. The process involves several principles that govern the effectiveness and efficiency of laser metal cutting. Here are the key principles:
- Laser Beam Generation: A laser beam is generated by exciting a medium, such as a gas mixture or a solid-state crystal, which results in the emission of photons. These photons are then amplified and directed into a beam using mirrors and other optical components.
- Beam Focusing: The laser beam is focused onto the metal surface using a lens system or a curved mirror. Focusing concentrates the energy of the beam into a small spot, increasing its power density and allowing precise cutting.
- Material Interaction: When the laser beam strikes the metal surface, it interacts with the material in several ways. The beam’s energy is absorbed by the metal, causing localized heating and eventually melting or vaporization. The type of metal and its thickness determine the specific interaction and the process parameters required.
- Melting and Vaporization: As the laser beam heats the metal, it causes localized melting. The molten metal is blown away by a gas jet, such as oxygen or nitrogen, which is directed at the cutting zone. In some cases, the laser beam can directly vaporize the metal, producing a cut without melting.
- Assist Gas: An assist gas, usually oxygen or nitrogen, is used to blow away the molten metal and create a clean cut. Oxygen is commonly used for cutting steel because it reacts with the hot metal, enhancing the cutting speed. Nitrogen is used for non-ferrous metals to prevent oxidation and ensure a clean cut.
- Kerf Width: The width of the cut, known as the kerf, is determined by the diameter of the focused laser beam. The smaller the focused spot, the narrower the kerf width, allowing for high precision cutting.
- Cutting Speed and Power: The cutting speed and power of the laser are critical parameters in laser metal cutting. Higher power levels enable faster cutting speeds, while lower power levels are suitable for thin or delicate materials. The selection of appropriate cutting parameters depends on the material type, thickness, and desired cutting quality.
- Precision and Accuracy: Laser metal cutting offers exceptional precision and accuracy due to the concentrated energy of the laser beam and the ability to control the beam’s movement. Computer numerical control (CNC) systems guide the laser beam along the desired cutting path, ensuring precise and repeatable cuts.
- Cutting Edge Quality: Laser metal cutting produces a high-quality cut with minimal distortion, heat-affected zone (HAZ), and burrs. The focused laser beam allows for fine and intricate cuts, resulting in smooth edges and minimal material wastage.
Overall, laser metal cutting combines the principles of laser physics, material interaction, and process parameters to achieve precise, efficient, and high-quality cuts in metal materials. It is widely used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and fabrication, due to its versatility and superior cutting capabilities.
Additional Services
- Product design services 2d, 3d
- Fabrication
- Gate and grill design using laser cutting
- Electric panel
- Sheet metal chassis
- Outdoor Cabinets
- Battery Racks
At, last, here we will see the few cutting work samples and also after going through all the laser cutting samples. We can easily analyze the laser cutting differences from the traditional cutting machines. For, getting more info and laser cutting works. You may contact us at Call/ WhatsApp: 9804-716-716.
Laser Cutting Samples